Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. It contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce and is mostly known as the master blueprint for life that constitutes the genetic material in all organisms.
History
DNA was first recognized and identified by the Swiss biologist Johannes Friedrich Miescher in 1869 during his research on white blood cells.
The double helix structure of a DNA molecule was later discovered through the experimental data by James Watson and Francis Crick. Finally, it was proved that DNA is responsible for storing genetic information in living organisms.
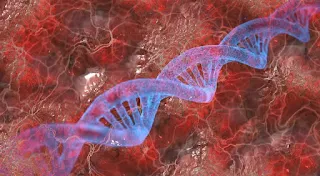
Structure
DNA is made of two polynucleotide chains (or strands) composed of simpler monomeric units called Nucleotides that coil around each other in opposite directions to form a double helix. These DNA strands are held together by hydrogen bond.
Nucleotides are the basic building block of DNA composed of:
- Nitrogen bases (cytosine[C], guanine[G], adenine[A] or thymine[T])
- A Sugar (deoxyribose) - the backbone of a DNA molecule
- A Phosphate group.
Base Pairing
Base pairs are essential for the DNA’s double helix structure, which resembles a twisted ladder.
They are paired together as A with T, and C with G; which is Adenine and Thymine, Cytosine and Guanine.The order of these nitrogenous bases determines the genetic code or the DNA’s instructions.
DNA Replication
Function
DNA is the genetic material that carries all the hereditary information. Apart from Storing Genetic Information, DNA is involved in:
- DNA Fingerprinting
- Transcription
- Replication
- Cellular metabolism
- Mutation
- DNA was First Discovered in 1869.
- DNA is contained in the chromosomes of a cell.
- All living things have DNA.
- Human DNA is 99.9% Identical
- DNA Contains Approximately 3 Billion Base Pairs.


Comments
Post a Comment
We will love to hear from you...
Share your thoughts with us!